Motor Services
Maintenance Program
Conducting scheduled preventative maintenance on your electric motor is essential to mitigate failures, enhance performance, ensure safety, and minimize unplanned downtime. However, understanding the specific requirements for maintaining your motor is crucial. This electrical motor maintenance checklist not only identifies early failure symptoms but also provides proactive maintenance recommendations to sustain optimal motor operation over its lifecycle.
An effective maintenance program includes meticulous record-keeping, empowering operators and engineers to discern patterns and anticipate issues before they escalate. By adopting a proactive approach to equipment maintenance, many potential problems can be preemptively addressed during scheduled downtime, thereby minimizing productivity losses.
The frequency of preventative maintenance depends on factors such as the motor’s age, operational hours, and criticality. For instance, in a manufacturing facility operating 24/7, performing this checklist every three months may be advisable. Critical motors may necessitate even more frequent maintenance, while older motors typically require more intensive upkeep compared to newer ones.
Motor Rewind
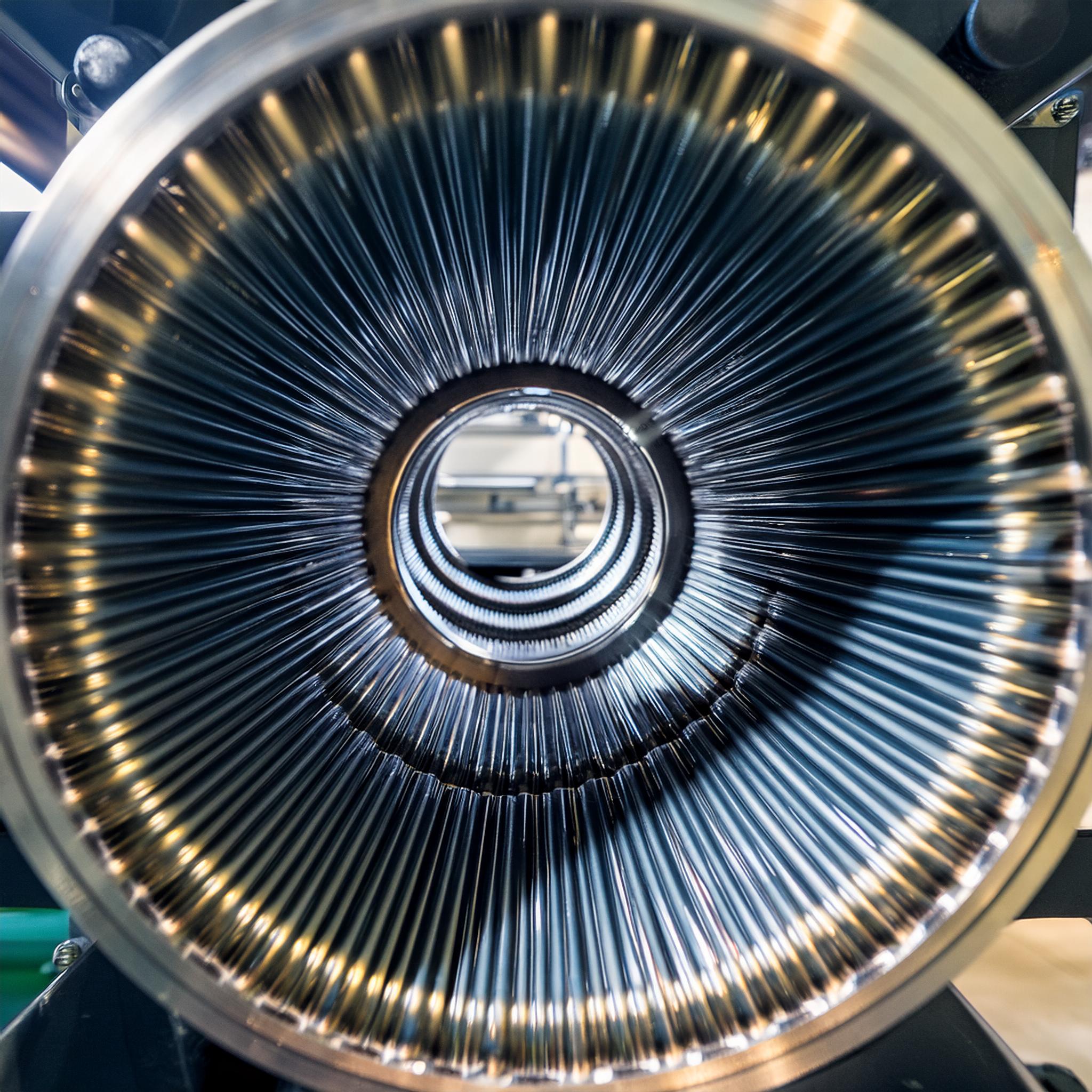
Rewinding an electric motor involves replacing or repairing the electrical windings within the motor. These windings, made of copper or aluminum wires, carry the electric current that creates the magnetic field necessary for the motor’s operation. Over time, factors such as wear and tear, overheating, or electrical faults can damage the windings, leading to motor inefficiency or failure.
The rewinding process starts with the careful removal of old or damaged windings. New windings are then installed, which may involve replicating the original number of turns or making adjustments to enhance the motor’s performance. The new windings are meticulously insulated and connected to the appropriate terminals to ensure optimal functionality.
Laser Alignment
In industrial applications, machinery is frequently interconnected through shaft couplings. Over time, misalignment of these shafts can occur, potentially causing mechanical failure, substantial energy loss, and production inefficiencies. Consequently, it is imperative to conduct regular shaft alignment checks.
Shaft alignment, or coupling alignment, involves aligning two or more rotating shafts along a common centerline. This process can be performed using various tools and techniques, including optical systems, lasers, dial indicators, calipers, and straightedges. Laser alignment is widely recognized as the most accurate and efficient method.
At AMED-US, we specialize in laser alignment services, ensuring the precision and reliability of your machinery for optimal operational performance and extended service life.
Electrical Testing Procedures
Conducting electrical testing and inspections is crucial for identifying early signs of deteriorating winding insulation, loose terminations, and preventing further degradation. This process can detect moisture within the windings, mitigating potential failures during startup.
Testing Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) for the stator and bearings helps eliminate false temperature readings from monitoring equipment, thus preventing nuisance shutdowns. Additionally, electrical testing verifies the functionality of space heaters, which are essential for preventing moisture ingress in motors during idle periods.
These inspections allow for the proactive maintenance of visible wear, rubbing, loose terminations, and failing taped connections, effectively preventing motor failures.
GET A QUOTECountries
Manufacturers
Happy Customers
Items in Inventory

